
A. 98 J
Incorrect. This is the gravitational potential energy at a height of 2 m.
B. 245 J
Correct! The kinetic energy gained is equal to the potential energy lost as it falls.
C. 343 J
Incorrect. This is the gravitational potential energy at a height of 7 m.
D. 62.5 J
Incorrect. You calculated one-half times the mass times the displacement squared; you need on-half times the mass times the velocity squared.
A. -12500 N
Incorrect. You calculated the change in the momentum of the car; you need to find the change in kinetic energy and divide by displacement.
B. -250 N
Incorrect. You divided the change in momentum by displacement; you need to divide the change in kinetic energy by displacement.
C. -156250 N
Incorrect. You calculated the change in kinetic energy; you need to divide this result by the displacement.
D. -3125 N
Correct! The change in kinetic energy is equal to the force times the displacement.
A. 4 m/s
Correct! The total momentum is conserved.
B. 0 m/s
Incorrect. This is the initial velocity of the 5,000 kg car.
C. 15000 m/s
Incorrect. This is the total mass of the system in kg.
D. 60000 m/s
Incorrect. This is the total momentum of the system in kgm/s.
A. 1.47 J
Incorrect. This is the gravitational potential energy, not the total mechanical energy.
B. 100.00 J
Incorrect. This is the kinetic energy, not the total mechanical energy.
C. 101.47 J
Correct! This is the potential energy added to the kinetic energy.
D. 5.00 J
Incorrect. The momentum of the ball is 5 kgm/s; you need energy.
A. conduction
Incorrect. Conduction is the transfer of heat by contact.
B. induction
Incorrect. Induction is the interaction between electric and magnetic forces in a circuit.
C. convection
Incorrect. Convection is the transfer of heat by upward movement of heated air.
D. radiation
Correct! This heat that is next to the side of the fire is transferred by radiation.
A. 4.9 m/s
Correct! Set the elastic potential energy equal to the initial kinetic energy.
B. 490 m/s
Incorrect. You need to convert from centimeters to meters.
C. 600 m/s
Incorrect. You calculated the acceleration of the box; you need the initial velocity.
D. 34.6 m/s
Incorrect. You calculated the force of the spring, not the energy.
A. 209,000,000 J
Incorrect. This was the initial energy of the water.
B. 167,200,000 J
Incorrect. This was the final energy level of the water.
C. 41,800,000 J
Correct! This is the heat loss.
D. 10,000 J
Incorrect. You forgot to multiply by the specific heat.
A. 1125 kgm/s
Incorrect. You calculated the kinetic energy.
B. 1960 kgm/s
Incorrect. You calculated the gravitational potential energy.
C. 3085 kgm/s
Incorrect. You calculated the total mechanical energy.
D. 150 kgm/s
Correct! Momentum is the product of mass and velocity.
A. 3.27 m
Incorrect. You set the potential energy equal to the initial kinetic energy; it should equal the change in kinetic energy.
B. 3.06 m
Correct! The change in kinetic energy equals the change in potential energy.
C. 0.20 m
Incorrect. You set the potential energy equal to the final kinetic energy; it should equal the change in kinetic energy.
D. 3.47 m
Incorrect. You added the initial and final values of the kinetic energy; you should have subtracted.
A student is conducting an investigation about the conservation of momentum. She records information about the mass and velocity of two lab carts before and after a collision.
|
|
Cart A |
Cart B |
|
Mass |
0.75 kg |
1.25 kg |
|
Velocity before the collision |
4 m/s right |
2 m/s left |
|
Velocity after the collision |
1 m/s left |
|
Which of the following should fill in the empty cell in the chart in order for momentum to be conserved?
A. 3.8 m/s right
Incorrect. The velocities are in the opposite direction from each other, so they have opposite signs.
B. 3.8 m/s left
Incorrect. The velocities are in the opposite direction from each other, so they have opposite signs.
C. 1 m/s right
Correct! The velocities are in the opposite direction from each other, so they have opposite signs.
D. 1 m/s left
Incorrect. The velocities are in the opposite direction from each other, so they have opposite signs.
A 0.015 kg bullet is traveling at 400 m/s when it hits a thick piece of wood. How far will the bullet penetrate into the wood if it feels an average stopping force of 24,000 N?
A. 0.05 m
Correct! The change in energy of the bullet equals force times distance.
B. 0.00025 m
Incorrect. You set the momentum equal to force times distance; you should have used kinetic energy.
C. 0.0167 m
Incorrect. You set the initial velocity equal to force times distance; you should have used kinetic energy.
D. 0.000125 m
Incorrect. You forgot to square the velocity when you calculated the kinetic energy.
A. 3.75 m/s
Incorrect. You calculated the average acceleration of the rock.
B. 1.25 m/s
Incorrect. Impulse is force multiplied by time; you used force divided by time.
C. 11.25 m/s
Correct! The impulse equals the change in momentum.
D. 45 m/s
Incorrect. You found the final momentum; you need to divide this result by the mass of the rock.
A. 5.0 m/s
Correct! The total work done equals the change in kinetic energy.
B. 24.5 m/s
Incorrect. You set the work you did equal to the change in kinetic energy; you need to use the total work.
C. 24.0 m/s
Incorrect. You set the work done by friction equal to the change in kinetic energy; you need to use the total work.
D. 34.3 m/s
Incorrect. The work done by friction should be subtracted from the work you did, not added.
A. 45 J
Incorrect. You calculated impulse, which is change in momentum; you need work.
B. 30 J
Correct! The work is the change in kinetic energy.
C. 5 J
Incorrect. You divided force by time; you needed to multiply by displacement.
D. 7.5 J
Incorrect. You need to multiply by displacement, not divide.
Two lab carts collide and stick together as shown below. What was the initial velocity of cart A?

A. -1.14 m/s
Incorrect. Be careful with positives and negatives.
B. 1.14 m/s
Incorrect. Be careful with positives and negatives.
C. -4.57 m/s
Incorrect. Be careful with positives and negatives.
D. 4.57 m/s
Correct! The cart must have been going right at 4.57 m/s.
A. 2.0 m/s
Correct! The elastic energy is transferred into both gravitational energy and kinetic energy.
B. 3.2 m/s
Incorrect. Some of the elastic energy is transferred into gravitational energy.
C. 4.0 m/s
Incorrect. You need to subtract the final gravitational energy, not add it.
D. 32.5 m/s
Incorrect. You forgot to square the compression when you calculated the elastic energy.
A. Conduction
Correct! Conduction is the transfer of heat by contact.
B. Induction
Incorrect. Induction is the interaction between electric and magnetic forces in a circuit.
C. Convection
Incorrect. Convection is the transfer of heat by upward movement of heated air.
D. Radiation
Incorrect. Radiation is heating the area directly around the Bunsen burner.
Which of the following is the temperature of water in a beaker?
A. The average velocity of the water molecules.
Incorrect. If the water is sitting in the beaker, then the average velocity of all of the water molecules is zero.
B. The average kinetic energy of the water molecules.
Correct! Temperature is the average molecular kinetic energy.
C. The total velocity of the water molecules.
Incorrect. Temperature is related to energy, not velocity.
D. The total energy of the water molecules.
Incorrect. This is the heat content, not the temperature.
A. 98 J
Incorrect. This is the work done when I lift it, but I also set it down.
B. 490 J
Incorrect. I do no work while walking down the hallway because the force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
C. 0 J
Correct! The total vertical displacement of the box is 0, so the total work is also 0.
D. 588 J
Incorrect. I do no work while walking down the hallway because the force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
A. 200 J
Incorrect. You calculated the momentum, not the kinetic energy.
B. 100 J
Incorrect. You forgot to square the velocity.
C. 1000 J
Incorrect. You forgot to multiply by one-half.
D. 500 J
Correct! The kinetic energy is 500 J.
A. Food coloring spreads out when added to water so that the color is eventually uniform.
Incorrect. Entropy in this case is increasing.
B. Two different temperature gasses come to the same temperature when mixed.
Incorrect. Entropy in this case is increasing.
C. A deck of cards is shuffled.
Incorrect. Entropy in this case is increasing.
D. A deck of cards is put in order by suit.
Correct! Entropy is decreasing when the deck is organized.
How much work is required to push a 10 kg box the frictionless ramp shown in the figure below?
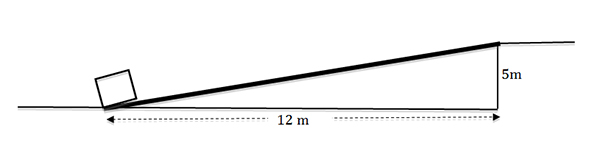
A. 490 J
Correct! The work done is equal to the weight multiplied by the height.
B. 1176 J
Incorrect. Use the height, not the horizontal displacement.
C. 1274 J
Incorrect. Use the height, not the length of the ramp.
D. 98 J
Incorrect. You need to multiply by the height of the ramp.
Which of the following Energy vs. Height graphs best models the kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy of an object thrown straight up?
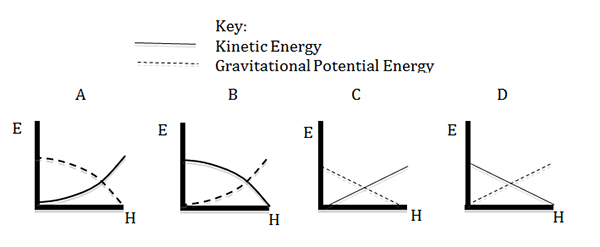
A
Incorrect. The gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to height.
B
Incorrect. The gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to height.
C
Incorrect. The gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to height.
D
Correct! The gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to height.
A. 2.9 m/s
Incorrect. Impulse is the change in momentum, not kinetic energy.
B. 4.2 m/s
Correct! Impulse is the change in momentum.
C. 0.47 m/s
Incorrect. Impulse is force multiplied by time, not divided.
D. 105 m/s
Incorrect. Velocity is momentum divided by mass, not multiplied.
A. 2.1 m/s to the right
Incorrect. The 50 kg student had a velocity of 3 m/s; you solved as if the 35 kg student had a velocity of 3 m/s.
B. 2.1 m/s to the left
Incorrect. The 50 kg student had a velocity of 3 m/s; you solved as if the 35 kg student had a velocity of 3 m/s.
C. 4.3 m/s to the right
Correct! The student will gain an equal and opposite momentum.
D. 4.3 m/s to the left
Incorrect. If the first student moves left, the second student must move to the right.
A. Conservation of mechanical energy
Incorrect. The system involved has several types of energy, not just mechanical.
B. Conservation of momentum
Correct! The hot gasses from the engine and the rocket gain equal and opposite momentum.
C. Conservation of mass
Incorrect. The conservation of mass does not explain the change in velocity.
D. Entropy
Incorrect. Entropy does not explain the change in velocity.
A. 2352 N
Correct! Her total change in energy was 4704 J, which requires 2352 N to stop in 2 meters.
B. 3920 N
Incorrect. She fell a total of 12 m, not 10 m.
C. 392 N
Incorrect. This is her weight, that is the force needed to stop her from accelerating.
D. 588 N
Incorrect. You treated the water like a spring and solved for the spring constant. You need the stopping force from the total work done.
A. 337.5 J
Incorrect. You found the kinetic energy, now add the potential energy.
B. 117.6 J
Incorrect. You found the potential energy, now add the kinetic energy.
C. 455.1 J
Correct! That is the total energy.
D. 45 J
Incorrect. You found momentum; you need to calculate potential and kinetic energy.
A. 29.4 W
Correct! That is the change in energy over time.
B. 3 W
Incorrect. You forgot to multiply by the acceleration due to gravity.
C. 11760 W
Incorrect. You multiplied by time; you need to divide by time.
D. 2.45 W
Incorrect. You divided by the displacement; you need to multiply.